Listen to Zooming In at The UnPopulist in your favorite podcast app: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Google Podcasts | RSS | YouTube
Landry Ayres: Welcome back to Zooming In at The UnPopulist. I’m Landry Ayres.
We find ourselves in a deeply troubling moment for American democracy, grappling with the stark realities of a political landscape increasingly defined by fear, performative cruelty, and a conscious assault on established norms and institutions.
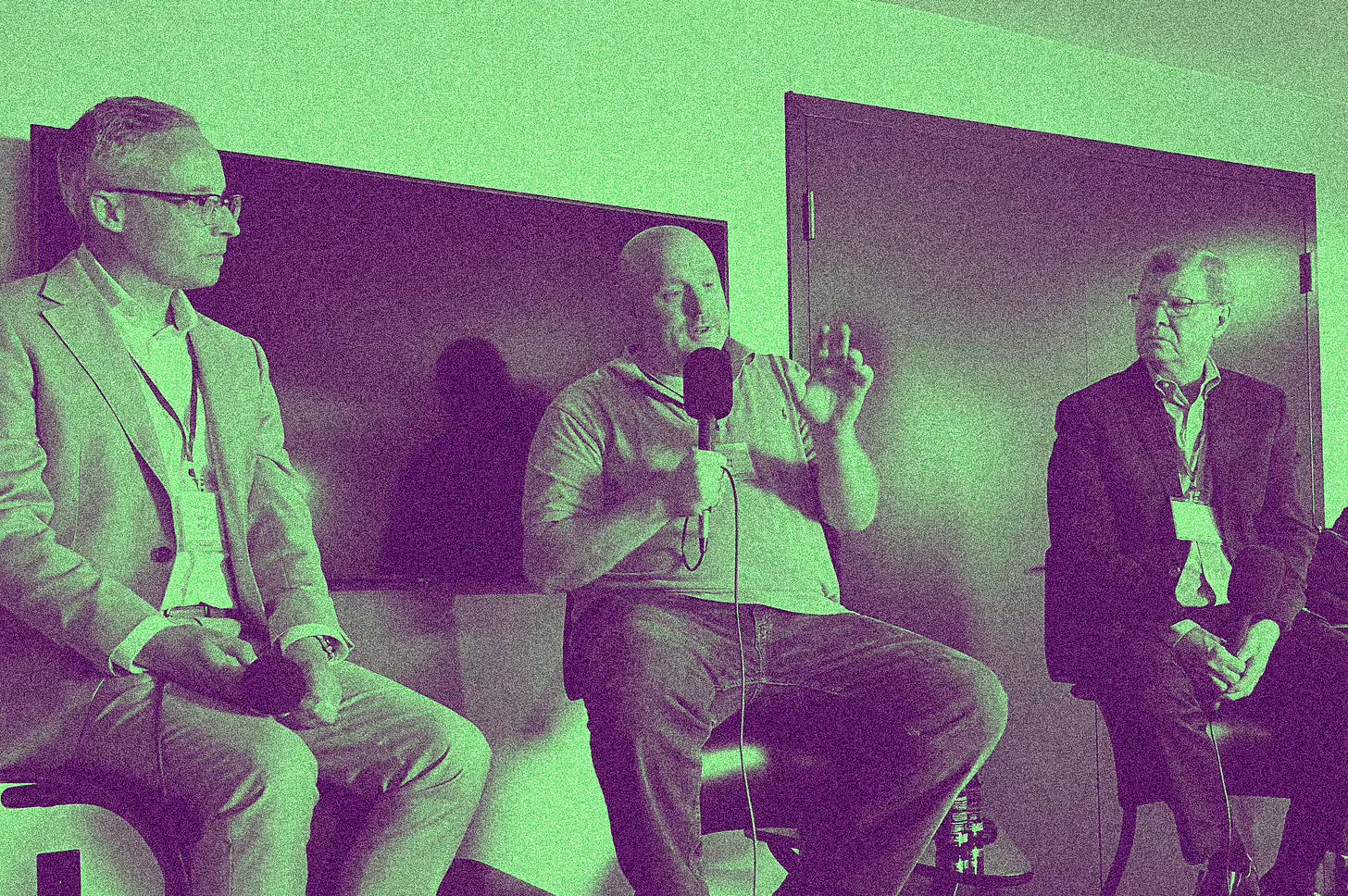
This special live recording from ISMA’s “Liberalism for the 21st Century” conference features host Aaron Ross Powell, as well as longtime observer of the militarization of police and author of the Substack, The Watch, Radley Balko, and co-founder and former contributor of The Bulwark, Charlie Sykes, author now of the Substack To the Contrary. They explore the mechanisms of this assault, how a manufactured crisis of fear is being weaponized by law enforcement, and the profound implications for civil liberties and the rule of law in America.
The discussion is insightful, if unsettling.
A transcript of today’s podcast appears below. It has been edited for flow and clarity.
Aaron Ross Powell: Welcome to a special live recording of The UnPopulist’s Zooming In podcast here at the “Liberalism for the 21st Century” conference in Washington, D.C. I am Aaron Powell and I’m delighted to be joined by Radley Balko and Charlie Sykes to talk about the situation we find ourselves in.
To me, the most striking image of Trump’s campaign, months before he was reelected, was from the RNC. Before that, there was the weird one of him in the construction vest. But the most terrifying image was the one depicting the “Mass Deportation Now!” signs and the sneering and cruel faces celebrating the culture that they were wallowing in. Those faces made me think, as I was looking at them, of the faces in photographs during the Civil Rights Movement of police officers about to inflict violence, turn on firehoses, let dogs loose, and so on. And it felt like what we are seeing now.
The “Mass Deportation Now!” images characterize not just the policies of Trump 2.0, but the attitude that they’re trying to inflict upon the country. It feels like a rolling back of what we achieved in the 1960s from the Civil Rights Movement—it feels like we’re in a retreat from that. This is a conscious attempt to roll that back. So I wanted to talk about that.
Radley, I’ll start with you. We’re sitting in D.C. right now as National Guard troops and members of all sorts of agencies are patrolling the streets. Is this surprising to you—the pace at which these nominally public servants, who are supposed to serve and protect, have embraced this role of violence and fear and chaos?
Radley Balko: I’m surprised at how quickly it’s happened. I’ve been talking to people about this day for the last 20 years. I’ve been warning about the gradual militarization of our police, which is something that has happened in conjunction with the drug war and then the war on terror over 40 or 50 years.
That debate was always about, “How militarized should our police be? How do we balance safety, and giving police officers what they need to protect public safety, with civil liberties and constitutional rights?” The fear was always that another Sept. 11 type event would cause what we’re seeing now—that there would be a threat, a threat that everybody acknowledges as a threat, that would cause an administration, states, mayors, to crack down on civil liberties. But it would at least be a threat that everyone recognizes as a threat. We would be debating about how to react to it.
When it comes to what’s playing out today, there’s no threat. This is all manufactured. This is all made up.
Your juxtaposition of those two images—the clownish image of Trump in the construction vest and the other one depicting this genuinely terrifying anger and glee a lot of his followers get from watching grandmothers be raided and handcuffed and dragged out of their homes—show the clownishness and incompetence of this administration juxtaposed with the actual threat and danger, the hate and vitriol, that we see from his followers.
We always hear that story about Ben Franklin after the Constitutional Convention: a woman comes up to him and says, “So, what is it, Mr. Franklin, do we have a republic or a monarchy?” And he says, “A republic, if you can keep it.” That phrase, of course, has been echoed throughout the ages. If Franklin were alive today, he would say, “You know, when I said that, I was worried about a Caracalla or a Sulla or a Caesar.” Instead it’s like, this guy, the guy that has to win every handshake, that’s who you’re going to roll over for?
I saw a lot of libertarian-ish people making this point before the election—that Trump’s not a threat, he’s a clown, he’s incompetent, he’s not dangerous. And you know what? He may be incompetent, but he’s put people around him this time who do know what they’re doing and who are genuinely evil.
So, on some level, this was the worst case scenario that I never really articulated over the years when I’ve talked about police militarization. This is actual military acting as police, not police acting as the military. But here we are and they’re threatening to spread it around the country to every blue city they can find.
Powell: He’s a clown, he’s rightfully an object of ridicule, he doesn’t know anything, he’s riddled with pathologies that are obvious to everyone except him. And yet it’s not just that he won, but that he effectively turned, not all of the American right, but certainly a large chunk of it into a personality cult.
Charlie, given that he seems to be a singularly uninspiring personality, what happened?
Charlie Sykes: Well, he’s inspiring to his followers.
Let me break down the question into two parts.
I was in Milwaukee during the Republican Convention, when they were holding up the “Mass Deportation” signs—which was rather extraordinary, if you think about it, that they would actually put that in writing and cheer it. It’s something that they’d been talking about for 10 years, but you could see that they were ramping it up.
But you put your finger on this culture of performative cruelty and brutality that they have embraced. Trump has made no secret of that. It’s one of the aspects of his appeal. For many, many years he’s been saying that his idea of law and order is to have cops who will break heads and inflict harm. He’s talked about putting razor blades on the top of the wall that Mexico was going to pay for. He’s told stories about atrocities. One of his standard stories—that I think the media just stopped even quoting—was about Gen. “Black Jack” Pershing in World War I taking Muslim terrorists and shooting them with bullets that had been dipped in pig’s blood. Totally bullshit—he made the whole thing up. But it was an indication of a kind of bloodlust. He’s talked about extrajudicial killings. He has expressed his admiration for strongmen like Duterte in the Philippines who have done this. He’s talked about having drug courts that would have trials and executions the same day. So this is not a secret.
What is really remarkable is the extent to which he’s communicated that to his base. I mean, there are Americans who legitimately have concerns about immigration and about the border. But what he’s also tapped into is this really visceral hatred of the other and the desire to inflict pain and suffering on them. I think that that is one of the ugliest aspects of his presence in our politics, and we saw that with the “Mass Deportation Now!” signs.
Now, the second part is how he is implementing all of this with his raw police state, his masked brute squads sent into the city streets. And, again, he’s made no secret of wanting to put active military troops into the streets of American cities. He was blocked from doing that in Trump 1.0, but obviously this is something that he’s thought about and wants to do. And one of the most disturbing parts about this is the embrace of these kinds of tactics and this culture by law enforcement itself. Radley’s written a lot about this. Donald Trump has gone out of his way, not only to defend war criminals, but also to defend police officers who’ve been accused of brutality. So he’s basically put up a bat signal to law enforcement that: The gloves are off. We’re coming in. There’s a new sheriff in town.
What’s happening in Washington, D.C. is just a trial run. He’s going to do this in New York. He’s going to do this in Chicago. He’s going to do this in one blue city after another. And the question is, “Will Americans just accept armed troops in their streets as normal?”
Now, let me give a cautionary note here: Let’s not gaslight Americans that there’s not actually a crime problem. I think Democrats are falling into a kind of trap because there are legitimate concerns about public safety. So the argument shouldn’t be: There’s no crime problem. The argument should be: This is exactly the wrong way to go about dealing with it. Having mass, brute squads on the street is one step toward really running roughshod over a lot of different rights—due process rights and other constitutional rights—that most Americans are going to be reluctant to give up. But we’re going to find out, because all of this is being tested right now.
Balko: I’d like to jump in on the crime point. I mean, crime is down in D.C. D.C. does have a comparatively high crime rate for a city of its size. There’s no question. It’s always been that way here. But the idea that there’s something happening right now that merits this response is what I meant when I called it a manufactured crisis.
I think it’s important to point out that, like you said, he’s always wanted to do this. This is just the reason that he’s managed to put his finger on and thinks is going to resonate.
“I’ve been talking to people about this day for the last 20 years. I’ve been warning about the gradual militarization of our police, which is something that has happened in conjunction with the drug war and then the war on terror over 40 or 50 years. That debate was always about, ‘How militarized should our police be? How do we balance safety, and giving police officers what they need to protect public safety, with civil liberties and constitutional rights?’ The fear was always that another Sept. 11 type event would cause what we’re seeing now—that there would be a threat, that everybody acknowledges as a threat, that would cause an administration, states, mayors, to crack down on civil liberties. But there would at least be a threat that everyone recognizes as a threat. We’d be debating about how to react to it. When it comes to what’s playing out today, there’s no threat. This is all manufactured. This is all made up.” — Radley Balko
I do think we need to talk about crime and about what works and what doesn’t. But I think it’s important to acknowledge that “crime” is just the reason that he’s found right now. This is something that he’s been planning to do forever. Like Kristi Noem said, it is basically about deposing the leadership in these cities. In Los Angeles, she said that their goal was to “liberate” it from the socialist elected leaders.
Sykes: I agree with you completely about that. I’m just saying that there is a danger of putting too much emphasis on the idea that there is not a crime problem—because in Chicago, there’s a crime problem, in New York, there’s a crime problem. People feel it.
And, I mean, didn’t Democrats learn a lesson in 2024 when there was inflation and they said, “Oh no, no, no, there’s not really inflation here. Let me show you a chart. You can’t think that the cost of living is a problem because here are some statistics that I have for you. There’s not really a problem at the border—if you think there’s a problem of immigration, a problem at the border, here, I have a chart showing you that there isn’t a problem.” Well, you can’t.
If the public honestly thinks that there is a problem at the border, that there’s a problem with inflation, and that there’s a problem with crime, it’s politically problematic to deny it because as David Frum wrote presciently in The Atlantic several years ago: If liberals will not enforce the border—you could add in, “or keep the city streets safe”—the public will turn to the fascists. If they think you will solve this problem and you’re pretending it does not exist or you’re trying to minimize it, they’ll turn to the fascists.
Balko: I don’t want to belabor this, but I just think it’s dangerous to concede the point when the premise itself is wrong.
So, Trump made crime an issue in 2016, right? Recall the American Carnage inauguration speech. When Trump took office in Jan. 2017, he inherited the lowest murder rate of any president in the last 50 years. And yet he ran on crime. I think that it’s important to push back and say, “Wait a minute, no, Obama did not cause a massive spike in crime. There was a tiny uptick in 2015, but that was only because 2014 was basically the safest year in recent memory.”
Trump is also the first president in 30 years to leave office with a higher murder rate than when he entered it. You know, I don’t think that presidents have a huge effect on crime, but Trump certainly does.
So, I agree with you that we can’t say crime isn’t a problem, but we can also point out that crime went up under Trump and that what he’s doing will make things worse.
Sykes: I think these are all legitimate points to make. It’s just that, Trump has this reptilian instinct to go for vulnerabilities. And one of the vulnerabilities of the progressive left is the problem of governance. If there is a perception that these urban centers are badly governed, that they are overrun with homeless encampments and crime and carjacking, then the public will see what he’s doing as a solution.
By the way, I’m making this argument because I think that we can’t overstate how dangerous and demagogic what he’s doing is. But I’m saying that this is going to be a huge fight. He’s going to go into Chicago where crime is just demonstrably a problem, and where I think the mayor has an approval rating of about 12 to 16%, and he’s going to say, “I am here with the cavalry.”
There’s got to be a better answer for this. There’s got to be a way to focus on the real threat to the constitutional order that he is posing, as opposed to arguing on his ground and saying, “No, no, don’t pay attention to crime, inflation, the border.”
And, again, I’m making this argument because this is one that I think the country really has to win. Otherwise we are going to see militarization and an actual police state.
Powell: Let me see if I can pull together some of the threads from the conversation so far, because I think there’s a nexus, or something that needs to be diagnosed, to see the way through.
When you [Charlie] were mentioning the bullets covered in pig’s blood, what occurred to me was ... I was a kid at the height of ’80s action movies. And that’s the kind of thing that the bad guys did in ’80s action movies. That’s the kind of thing that justified the muscular American blowing them up or otherwise dispatching them.
There’s been a turn, now, in that we’re seeing behavior from Americans that they would have at one point said, “This isn’t who we are.” The Christianity that many Americans hold to, this is not the way that Jesus tells them to act. There’s been a shift in our willingness to embrace this sort of thing, and it’s behavior that I would have expected to horrify basically everyone watching it happening.
And it is—his approval readings are declining rapidly. It is horrifying a lot of people—but fewer than I would have hoped. One of you mentioned that, on the one hand, there’s the cruelty, but there’s also the fear—and those are feeding into each other. And what I wonder is, yes, there’s crime, but at the same time, if your media consumption habits are those of a committed Trump supporter, you are being told constantly to be afraid that everybody outside your door, except for the people who you recognize, or maybe the people who share your skin color or speak with the same accent you do, is a threat to you and your family.
I see this with members of my own family who are Trump supporters. They are just terrified. “I can’t ride the subway. It’s too scary to ride the subway.” Or, “I go out in D.C. and I see youths doing the kinds of things youths do, and now I don’t feel safe having my family there.” We don’t have a war. We don’t have a crisis. But we’ve told a huge portion of the country, “You should be afraid of every last thing except your immediate family and that guy who now rules the country.” And the crime rates are part of it. It’s like, “You should be scared of every single one of these cities.”
Sykes: It’s a story. One of the speakers today was talking about the power of stories, that demagogues will tell a story. And a story of fear and anger is a very, very powerful story that you can’t counteract with statistics. You need to counteract it with other stories.
“This culture of performative cruelty and brutality is one of the aspects of his appeal. For many years he’s been saying that his idea of law and order is to have cops who will break heads and inflict harm. He’s talked about putting razor blades on the top of the wall that Mexico was going to pay for. He’s told stories about atrocities. He would tell the story about Gen. ‘Black Jack’ Pershing in World War I taking Muslim terrorists and shooting them with bullets that had been dipped in pig’s blood. He’s talked about extrajudicial killings. He has expressed his admiration for strongmen like Duterte in the Philippines who have done this. He’s talked about having drug courts that would have trials and executions the same day. What is really remarkable is the extent to which he’s communicated that to his base. He’s tapped into this really visceral hatred of the other and the desire to inflict pain and suffering on them. I think that that is one of the ugliest aspects, and we saw that with the ‘Mass Deportation Now!’ signs.” — Charlie Sykes
Part of the problem is that Trump has made that narrative. So, for example, you have members of your family who are Trump supporters. My guess is that they could name the young women who had been raped and murdered by illegal immigrants. Because, I mean, on Fox News, this is happening all the time, right? On Fox News, illegal immigrants are criminals. “Look at the crimes they are committing.” They tell that story in the most graphic way possible, and then turn around and say, “If you oppose what Donald Trump is doing, you are defending these ‘animals’”—as Trump described them.
It is deeply dishonest. It is deeply dangerous. But it is potent. And we ought to look at it in the face and recognize how he is going to weaponize those stories and that fear, which is really the story of our era now. We’re living in this era of peace, prosperity, general safety—and yet he’s created this “American carnage” hellscape story.
Balko: Yeah, I also think there’s this weird paradox of masculinity in the MAGA movement. It’s not about masculinity—it’s about projecting masculinity. It’s about co-opting aspects of masculinity. And it’s like, “We’re the manly men. We need men to be men again. And that’s why we support men who sexually assault and sexually harass women. And, at the same time, we’re all going to genuflect and debase ourselves in front of this 79-year-old man, because he’s our leader and we need to let him insult our wives. And we’re also scared to take the subway.” I think there were 10 murders last year in the New York city subway. The subway is one of the safest public spaces you’ll find anywhere. But you’ll regularly see MAGA people go on Fox News and talk about how scared they are of it.
I mean, I don’t know how persuadable any of MAGA is, but I do think pointing out the sheer cowardliness might resonate. When Markwayne Mullin goes on the Sunday shows and says he doesn’t wear a seatbelt anymore because he’s afraid he’ll get carjacked and he needs to be able to jump out of his car quickly ...
Sykes: ... He actually did say that.
Balko: Yeah. And, I don’t know what the stats are, but it’s something like you’re 40 or 50 times more likely to die in a car accident than you are in a carjacking. So, you know, he’s sealing his own fate, I guess.
But I do think that maybe there’s something to appealing to their lack of masculinity when they try to push some of these narratives.
Sykes: Well, yeah, I do think there are narratives out there.
We have National Guard troops here in Washington, D.C.—where were they on Jan. 6th? Why did the president not bring them in then? We had one of the greatest assaults on law enforcement. So we can call bullshit on Donald Trump being the “law and order,” “back the blue” president.
One of the first things he did when he took office was issue the blanket pardons to all the rioters and seditionists who not only assaulted the Capitol, but specifically the ones who attacked police officers. We can stand up and say, “I don’t want to be lectured by the man who gave the Get Out of Jail Free card to the people who tased and bear sprayed police officers in this city. Not to mention,”—before he brings up the whole “defund the police” thing—“the man who right now is dismantling the nation’s premier law enforcement agency, the FBI.” Because all of these FBI agents who are being gutted or tasked with hassling homeless people in Washington, D.C., you know what they’re not doing? They are not investigating child sex trafficking. They are not engaging in any anti-terrorism activities.
So, what you do is call them out, saying, “You are not making this country safer. You are not the ‘law and order’ president. You are a convicted felon. You in fact have freed and celebrated people who actually beat cops.” If Barack Obama would have pardoned someone who had attacked police officers, the right would have been utterly incandescent. And yet Donald Trump does it and he’s not called out on it.
I understand that there are some who are reluctant to say, “Well, no, we’re actually the party of law and order. We’re actually the party of public safety.” But you hit him right in what I think is a real vulnerability.
Balko: One of the guys who literally told Jan. 6 rioters to kill the police is now a respected senior member of the Justice Department, whereas the guy who threw a sandwich at a cop is facing a felony charge. That is Trump’s approach to law enforcement.
Sykes: I always hate it when people go on TV and say, “This should be a talking point.” But that ought to be a talking point. Don’t you think everybody ought to know his name? We have the video of Jared Wise saying, “Kill ‘em! Kill ‘em!” and calling the police Nazis. And he is now a top official in Donald Trump’s Justice Department.
Powell: This is my concern, though—and this allows me to belabor my Civil Rights Movement point some more. One of the reasons that the anti-civil rights movement, the counter-movement, was as vicious and as ugly as it was is because it was a group of people who felt like they had a status level by virtue of being white, of being men. As they saw things, “If we help minorities and others rise up, that lowers the baseline status that I have.” So they wanted to fight back. It was, “I’m going to keep these people down because it keeps me up.” And when Radley said that they’re “projecting masculinity,” I think that’s a big part.
A big part of the appeal is, “Now I’m seeing guys like me dominating. Now I’m seeing guys who are from my area or share my cultural values or dress like me or are into the same slogans or have the same fantasies of power as I do, or just aren’t the coastal elites with their fancy educations and so on, dominating.” And my worry is if that’s what’s driving a lot of it—that urge to domination coupled with the fear, which I think then allows them to overcome any barriers they have to cruelty—if you marry, “I can have power” and “I’m scared of these people,” that to them justifies their actions in the same way that it does the action movie heroes killing the guys who put the pig’s blood on bullets. It becomes justified to inflict cruelty upon those they hate.
My worry is if you go after them in that way, it feels like, “Okay, now what you’re saying is these guys who look like me, who were dominating, don’t actually deserve it.” I don’t think that means that we stay away from it, but I think it risks triggering even more of this, “What I want is for it to be my boot on people’s necks and I want them to stop putting me down. And I want them to stop telling me that I’m not good, that I’m incompetent, that it’s not okay for me to beat my wife” (or whatever it happens to be). Trump is like an avatar for very mediocre men.
Sykes: Well, I wouldn’t use that as a talking point.
Balko: A few years ago, I wrote a piece about a Black police chief who was hired in Little Rock by a mayor who ran on a reform platform and this police chief had a good record. He was in Norman, Okla. before that—he was the first Black chief in Oklahoma. And he was not a progressive by any means, but he was a reformer in that he wanted things to be merit-based and Little Rock has a really strong white police union. I say that because they also have a Black police union, because the Black officers didn’t feel like they were represented by the white union.
One of the first things that Chief Humphrey did was make the promotional interviews, that you get to move up through the ranks, blind. So you didn’t know who you’re talking to. If you were white, you didn’t know if it was a fellow white person you were interviewing. Most of the people in charge were. The result of removing race from that process was that more Black officers were getting promoted than before. And I wrote about him because he ended up getting chased out of town. They hit him with fake sexual harassment charges; the union claimed he was harassing white women. Basically, they exerted their power and managed to chase him out.
But one of the things he told me when I interviewed him was—and other people have said different versions of this—that when your entire life you’ve been the beneficiary of racial preferences as a white person, as happened in this country for most of its existence, meritocracy looks a lot like racial discrimination. Because things that you got just simply because you were entitled to now you have to earn. And that looks like, “Hey, this Black guy is getting this job over me. And that’s not right. Because my dad got that job over the Black guy and his dad got the job over the Black guy.”
And I think this backlash that we’re seeing against DEI—I’m sure there are parts of this country where DEI was promoting unqualified people just to have diversity, and I do think there’s there’s value in diversity for diversity’s sake—is white people, who have been benefiting from our racial hierarchy system that’s been in place since the Founding, were starting to see themselves passed over because we were now moving to a merit-based system and they saw that as discrimination. That’s a big part of the backlash.
I don’t know what the solution is. I don’t know that we just re-impose all of the former policies once Trump’s out of power, if he’s ever out of power. But I do think that there is value in diversity for diversity’s sake. Obviously I don’t support strict quota systems, but I do think it’s important to make that point that addressing historical injustices is critical.
We went to the art museum in Nashville the other day and they had a whole exhibit about Interstate I-40 going through Nashville. It was supposed to go through this industrial area where there were no neighborhoods or private homes. And the Tennessee legislature deliberately made it run through the wealthiest Black neighborhood in Nashville and destroyed about 80% of Black wealth in the city. That was 1968—that was not 1868. That’s relatively recently that you’re destroying a ton of wealth. And you can find that history in every single city.
I think a big part of this backlash is not knowing that history—and only knowing what’s happening now and experiencing it out of context. For those people, it feels like reverse discrimination.
Sykes: So, yes, a lot of this is true. But it’s not the whole story. In the state of Wisconsin, overwhelmingly white voters voted for Barack Obama, a Black man, twice in a row before voting for Donald Trump. So we do have that long, deep history of racism, but then also an America that I think was making some progress. I’m just going to put this out as a counterpoint: I think that if people were appealing to the “better angels of their nature,” a lot of these people would not be buying into the cruelty, the brutality, the racism. Instead, we’re appealing to their sense of victimization.
But let’s be honest about it. We moved from a Civil Rights Movement that was morally based on fairness and the immorality of discrimination to one that increasingly was identity politics that morphed into DEI, which was profoundly illiberal. What happened was a lot of the guys we’re talking about were thinking not just that they want their boots on people’s head, but they’re constantly being told that they were bad, that their contributions were not significant. There were invisible tripwires of grievance—what you could say, what you could do, the way you had to behave. In the before times, a lot of the attacks on free speech and the demands for ideological conformity on university campuses were not coming from the illiberal right—they were coming from the illiberal left.
And as I’m listening to the speakers at this conference talk about the assault on liberalism, I think one of the questions we have to ask—and maybe this is a little meta—is why it was so brittle. Well, it was brittle because it was caught in a pincer movement by the illiberal left and the illiberal right. My point is that a lot of this reaction is in fact based on racial animus, but there’s also a sense that I hear from a lot of folks, a sense of liberation that they feel, that the boot was on their necks and is now being taken off, that they’re not having to go to these highly ideological DEI training sessions where they were told how terrible and awful they were all the time. And how, if you believed in a race-blind society, that was a sign you were racist. If white women actually were moved by stories of racism and wept, that was white women’s tears. This was heavy handed.
“I do think the people who signed off on extraordinary rendition and snatching people off the street and sending them to a literal torture prison in El Salvador, those people need to be criminally charged. But I also think there need to be civil society repercussions. There are so many people in media—pundits, politicians who know better—who have a long record of pointing out how dangerous Trump was and then turned on a dime and started supporting him. I don’t wish any physical harm on those people. I don’t think any of those people should be put in prison. But I think those people should never be trusted as public intellectuals.” — Radley Balko
So there was a backlash that was going to be inevitable. What’s tragic is the way that it has been co-opted by the people who have really malign motives, who are not acting out of good will—the Stephen Millers who have figured out a way to weaponize this. But that line that goes from the racism of 1957 to the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s, to a broad-based civil rights consensus—and, again, there’s caveats in all of this—to identity-based politics. Let’s be honest about it. That was not without sin. That was not without problems.
Balko: So, I agree that there was I guess what you could call an illiberal approach to a mutual exchange of ideas on college campuses. There was a lot of shouting down of conservative speakers. In some cases, there were invitations revoked to valedictory speeches. There was some cutting off of funding for conservative speakers. But I want to make sure we’re not delving into false equivalences here. I mean, the boot that you’re talking about, Charlie, was a metaphorical boot, and we’re talking about a very literal boot now.
Sykes: Absolutely. That distinction is a significant one.
Balko: So, my preferred way of expressing my disagreement with someone isn’t to shout them down. I will say, though, that protest is a form of speech. I think, even to some extent, interrupting speeches that are particularly problematic or extremist is a form of speech. It’s not one that I personally would engage in. But the type of censorship we’re seeing now is direct. It is government censorship. It is not a violation of the spirit of free expression that we were seeing on college campuses before.
Sykes: Oh, it was more than just that kind of violation. You had universities that required people to sign a DEI statement where they had to make ideological commitments in order to get a job. I mean, this was very heavy handed. There were no literal boots, but ... I like Jonathan Rauch’s analogy that the illiberalism of the left is still a real problem, but it’s like a slow-growing cancer. Right now, what we’re facing with the illiberalism of the right is a heart attack. We have to deal with the heart attack right now, but let’s not pretend that everyone who objects to some of the things that were happening are doing so because they are just vile, white racists.
This is part of the problem. People spent decades accusing others of being racist on flimsy grounds. If you support Mitt Romney, you’re a racist. If you support tax cuts, you’re a racist. You know what happened? I come from this world and there was a time when to be called a racist was the worst thing you could possibly say about somebody. And it got to the point where, literally, if you were in favor of school choice, you were racist; in favor of tax cuts, you were racist. If you voted for a Republican … John McCain was a racist, George Bush was a racist. So when the real thing came along, guess what people said? They just rolled their eyes, shrugged, and said, “We’ve heard this before.” I mean, it was crying wolf for decades.
And I’ve had these conversations when I would say, “How can you support someone who is just espousing this raw, vicious racism about Haitians eating dogs?” You know what I would get? “Oh, we’ve been hearing this for 20 years. Literally everyone I know has been accused of being a racist.”
So we need to come back to a consensus. If we’re going to restore that liberal consensus, we’re going to have to say, “This is acceptable behavior. And this is not acceptable behavior.” But we are not going to use these labels to vilify. The politics of contempt is just not helpful. It is not helpful to tell people, “By the way, I think you’re an idiot. I think you’re stupid. I think you’re racist. Would you like to hear my ideas about taxes now?” It doesn’t work. And I think that one of the things that, tragically, Trump has tapped into is the sense that these elites look down on you.
So, Aaron, when you say that this is the revolution of mediocre men, not helpful. Now, some of them are mediocre. I certainly agree. I write about mediocre people all the time—but, again, the politics of contempt is not the way to get ourselves out of this.
Powell: I think there’s a distinction between messaging and diagnosis. And if we’re to understand how we got here, or the kinds of beliefs or values that can lead someone ... and I don’t mean, you’ve been a partisan Republican voter for your entire life, and you come from a family of this, and you pulled the lever for Trump, but you’re mostly an uninformed voter, which is a lot of people—I mean, the people who are cheering on Stephen Miller, they’re in a different category. So it might be that, if you have one of those people in front of you, the message is not to say, “There’s a broken set of morals at play here,” or “there’s a cramped view of humanity at play here,” because they’re not going to hear that in the moment.
But if we’re to understand how we got here and what we’re up against, I think we have to be fairly clear-eyed about the fact that the [Trumpian] values that we’ve discovered over the last 10, 15 years have much more appeal and purchase among a lot of Americans than I think any of us had really expected or certainly hoped, and then figure out how to address that. And, again, it’s not everybody—but it’s more than I would like. If those values are central to someone’s being, and the way that they view others around them and the way they relate to their fellow man, then I think a lot of the less condemning arguments also won’t find purchase because, ultimately, it’s not a policy difference. It’s a, “I want a crueler world.”
Sykes: This is where I think the argument that says, “Let’s look at this cruelty. Let’s look at this brutality. Let’s look at the Stephen Millers” ... believe it or not, I actually think it’s potent to say to somebody, “Do you want to be like that? Is that really what you want America to be? You’re better than that.” And then, “Let me tell you the story of decency.”
The story that we heard earlier today about how neighbors who are Trump voters will be there if your house is burning down or your father dies ... you appeal to that innate decency and say, “Do you really want this cruelty?” This is what’s lacking, I think, on the right and in the Republican Party right now: people who say, “Okay, you may want less taxes, smaller government, a crackdown on street crime, less illegal immigration ... but is this who you want to be?” Show them the masked officer who is dragging the grandmother away. I do think that there is the better angel that says, “No, that is really not the American story.” You have to appeal to them as opposed to just condemn them. I’m not sure we’re disagreeing, but I actually think that that’s potent.
Balko: I think there is not only room for ridicule when you’re up against an aspiring authoritarian, but a lot of history shows it’s often one of the few things that works because they really hate to be disrespected.
I agree with Charlie that I don’t think it’s necessarily productive to make fun of people who have been tricked or who have been lied to, but I also think it’s worth pointing out that Trump has contempt for his own supporters. I mean, one of the great ironies of our time is that when Trump would need a boost of self-esteem, he would go hold a rally in a state that, before he ran for president, he would never have been caught dead in. He grifts from his own supporters. His lies about Covid got his own supporters killed at higher rates than people in states that didn’t vote for him. But I agree that it doesn’t serve much benefit to denigrate people.
Sykes: But do ridicule the people who are doing it. I mean, don’t get me wrong. South Park is doing God’s work right now.
Balko: Absolutely.
Powell: What, then, is the way forward?
“This is part of the problem. People spent decades accusing others of being racist on flimsy grounds. If you support Mitt Romney, you’re a racist. If you support tax cuts, you’re a racist. You know what happened? I come from this world and there was a time when to be called a racist was the worst thing you could possibly say about somebody. And it got to the point where, literally, if you were in favor of school choice, you were racist; in favor of tax cuts, you were racist. If you you voted for Republican. John McCain was a racist. George Bush was a racist. So when the real thing came along, guess what people said? They just rolled their eyes, shrugged, and said, ‘We’ve heard this before.’ I mean, it was crying wolf for decades.” — Charlie Sykes
Let’s assume that democracy survives this current moment and that we somehow put Trump behind us. We can’t go back to the status quo before this. We can’t just say, “We’re going to go back to the kind of politics we had during the Biden administration.” That seems to be off the table. We need something new. We need a new direction. What does that look like?
Sykes: I honestly do not know at this point. And I don’t think anybody knows. But I do think that we ought to remember, because we throw around the term “liberal democracy” a lot, that democracies are not necessarily liberal. Democracies are not necessarily kind. And I think we need to go back to things like the rule of law.
I think it’s going to involve some kind of restoration of balance in society. The damage that’s being done now is so deep and some of it is so irreparable that I’m hoping that there will be a backlash against it, that there will be a pendulum swing back towards fundamental decency. And even though we keep talking about democracy a lot, I think we need to start talking about freedom and decency a little bit more.
You know, I was listening to the Russian dissident who spoke tonight and he asked us to imagine what it’s like trying to create a democratic society in Russia with all of their history and all their institutions. As bad as things are for us, we have a big head start. We still have an infrastructure, compared to what he is up against. We still can restore, I think, that fundamental decency and sense of freedom and equality before the law.
Balko: I also don’t know exactly what it’s going to look like. I will say this: I think one of the big reasons why we are where we are today is that there wasn’t a proper reckoning, and no real accountability, after the Civil War and Reconstruction. It’s been the same with Jan. 6. There was no real accountability. The Democrats waited too long for impeachment. The DOJ was slow.
I do think there have to be repercussions. I’m not saying that we throw everybody in the Trump administration in prison, but I do think the people who signed off on extraordinary rendition and snatching people off the street and sending them to a literal torture prison in El Salvador, those people need to be criminally charged.
But I also think there need to be civil society repercussions. There are so many people in media—pundits, politicians who know better—who have a long record of pointing out how dangerous Trump was and then turned on a dime and started supporting him. I don’t wish any physical harm on those people. I don’t think any of those people should be put in prison. But I think those people should never be trusted as public intellectuals. We shouldn’t employ them in that realm. I think they should be able to earn a living. I don’t think they should earn our trust.
I have zero confidence that that’s going to happen. But I can personally say that I have no interest in participating in events like this with those people. I have no interest in giving those people any kind of legitimacy because they tried to take our birthright away from us, which is a free and democratic society—the country that, for all its flaws, has been an exemplary country in the history of humankind. They literally are trying to end that. And I don’t think you just get to walk away from that and pretend like it never happened.
Sykes: I totally agree.
Powell: With that, thank you, Radley. Thank you, Charlie.
© The UnPopulist, 2025
Follow us on Bluesky, Threads, YouTube, TikTok, Facebook, Instagram, and X.
We welcome your reactions and replies. Please adhere to our comments policy.